Breast Enlargement using implants
Breast Enlargement – Breast Augmentation is an operation used to enlarge and usually improve the shape of breasts, using implants. Psychological studies have shown that patients who have successful breast enlargement often have a significant boost in their self-confidence and are much happier about wearing revealing clothing and more comfortable with their sexuality.
The consultation
The consultation can be quite lengthy as there are many issues to discuss. Sometimes you may need to return for a second consultation to finalise details. You will be asked about your medical history. This will include information about any medical conditions, drug allergies, medical treatments you have received, previous operations, including breast biopsies, and medications that you currently take. You will be asked whether you have a family history of breast cancer and about results of any mammograms. Your breasts will be examined and photographs will be taken for your medical records. Factors that need to be considered are; the size and shape of your breasts, the quality of your skin and the placement of your nipples. If your breasts are sagging, a breast lift may be recommended as well as a breast enlargement If you are planning to lose a significant amount of weight, be sure mention it as it may be better to stabilize your weight prior to undergoing surgery. It is important to point it out if you plan getting pregnant in the future. Pregnancy can alter breast size in an unpredictable way and could affect the long-term results of your breast augmentation. There is no evidence that breast implants will affect pregnancy or your ability to breast-feed, but if you have questions about these matters, don’t hesitate to ask. If you are a smoker, you will be asked to stop smoking well in advance of surgery. Aspirin and certain anti-inflammatory drugs can cause increased bleeding, so you should avoid taking these medications for a period of time before surgery. There may be additional preoperative instructions at the time of consultation.
GDPR
Your data is stored according to GDPR guidelines. Photographs are required as essential records and are an integral part of the planning process for breast augmentation. While chest photographs are usually not recognisable as you, these photographs are regarded as highly sensitive and confidential and therefore cannot be released into the public domain. We ask for your consent to store your photographs. Your images are stored on 2 standalone secure encrypted hard drives. Additional and specific consent is required to publish or place your images on the internet.
Breast implants
Breast implants are made of an outer layer of silicone, but may be filled with silicone gel, salt water or a combination of both. Implants filled with soya oil have been withdrawn from the market. After many modifications to implants over the years, such as surface texturing, polyurethane coating, different contents such as soya oil, most breast surgeon have returned to the original type of’ tried and trusted’ implants ; SOFT SILICONE FILLED IMPLANTS WITH A SMOOTH SURFACED SHELL.
The silicone inside the breast enlargement implant can be in liquid form (gives a very soft and natural feel) or less liquid jelly ‘cohesive’ silicone (Gummy bear), which feel more firm. Many firm /shaped implants are no longer used as they require a textured surface to hold the implants in position and prevent them rotating. However this problem may be overcome by the use of microtextured shaped implants.
Textured Implants , including Biocell (No longer being used)
Implants can have a smooth or textured surface. For years it was thought that textured implants have a lower capsular contracture rate but this has recently been questioned and this issue has caused great controversy in 2019, (see complications).
Another type of implant which is claimed to have a lower capsular contracture rates are the polyurethane coated implants. These implants may have a similar risk to Biocell in terms of ALCL ,(see complications)
More recently , microtextured implants have been developed that have the advantages of textured implants but less risk of ALCL. This means that shaped or anatomical implants can be used in cases where necessary.
PIP implants (no longer being used)
PIP implants were a range of breast implants which are now regarded as faulty. They were not produced according to the strict medical standards that all other implants are subject to.
They had a tendency to rupture and the contents were composed of non-medical grade silicone , which contained impurities. It is thought that only some product batches were faulty but none the less it has been recommended by most authorities that these implants should be replaced to avoid a possible risk of cancer.
Manufacturers suggest that the life expectancy of breast implants is approximately 10 years, although implants can stay in without problems for a much longer time.
Are there alternatives to breast implants?
Using padded bras or inserts can make your breasts appear bigger with a better shape. Natural breast enhancement pills that contain phytoestrogens (plant hormones that copy natural hormones) may help to increase the size of your breasts. However, these pills have not been properly tested, may increase the risk of certain cancers and may cause you to put on weight. You may benefit from using the Brava® system that involves using a special bra to apply gentle suction to your breasts. The continued suction may stimulate new tissue to grow. However, there is little evidence that the system is effective and the long-term results are not known.
Lipofilling
Fat grafting is a very promising alternative which is being used for small augmentations in some centres. The woman’s own fat is harvested from the abdomen or thighs and re-injected into the breasts. The problem with this treatment is that it usually requires multiple procedures to achieve a modest enlargement and is therefore very expensive. The other difficulty with this technique is that many patients have very little body fat. However, results when successful can be very natural and soft with none of the long term complications of implants.
The breast enlargement operation
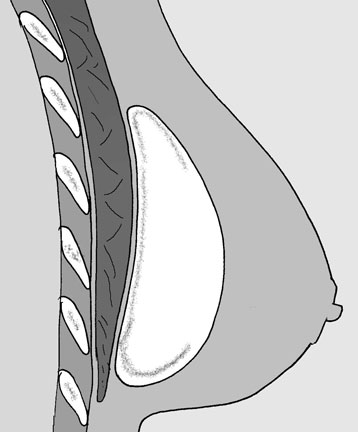
Implants are usually inserted through a cut in the crease under the breast (inframammary fold). Alternatively, the incisions may be made around the areola or in the armpit however these techniques have lost popularity and are usually reserved for special circumstances. Very great care is taken to maintain sterility during the operation. Contamination of the implant with certain bacteria will cause infection requiring removal of the implant in many cases. It is thought that very low-level contamination with relatively harmless skin bacteria may be the cause of capsular contracture. Additional sterile precautions are therefore taken when doing implant surgery. (Antibiotics, double gloving /changing gloves, double prepping, breast pocket washout with saline and antibiotics, minimal implant handling, nipple covers).
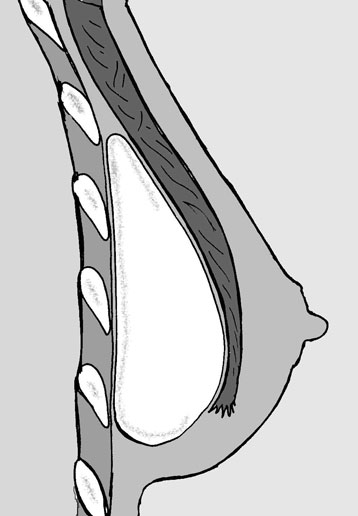
A pocket is then created for the implant which is either under the breast itself or behind the muscle on which the breast lies. In my practice, implants are most often placed behind the breast as this gives a very natural result. However in very thin patients, who have very little breast tissue, (particularly if they have not had children), it may be better to place the implants behind the muscle to avoid the outline of the implants being obvious.
The surgery takes approximately one and a half hours and is usually done under general anaesthetic. The implant is placed in a pocket either directly behind the breast tissue (left) or underneath the pectoral muscle which is located between the breast tissue and chest wall. Individual factors and personal preferences will help you and your plastic surgeon to determine your appropriate breast size, the location of incisions, and whether the implants will be placed on top of or underneath the chest muscle.
Post operative recovery
Like all operations, there will some postoperative pain which is usually well controlled by pain killers. Each patient experiences very different degrees of pain but in general patients don’t find it particularly bad. It is often sore for a few days along the breast bone, particularly if the implant is placed under the muscle. Moving your arms can be uncomfortable for two to three weeks after the operation but this gradually settles. The breasts are often swollen and tense to begin with but this settles down and the breasts become more natural looking after a few weeks. Sometimes there can be bruising around the cleavage and under the breasts but this settles within two weeks. Most women will have reduced feeling (sensation) in the breast and nipple after the operation. While much of the feeling returns within a year in some cases the loss of feeling can be permanent.
Augmentation Mastopexy
Many Women have issues with the shape as well as the size of their breasts. This is particularly true for women who have had children and lost breast volume afterwards. Their breast skin is stretched during pregnancy and breast feeding and when the breast volume shrinks, they are left with a loose droopy envelope of skin which can be flat with the nipples too low or even pointing downwards. This is called breast ptosis and is much more difficult to correct.
These patients have too much skin and simply placing an implant into the breast will not work. Placing an implant on its own will create a ‘ball in a sock ‘ look which results in a poor aesthetic outcome.
The only solution in these circumstances is to remove some of the excess skin and perform a breast lift, also known as a mastopexy.
However , doing a mastopexy at the same time as placing an implant dramatically raises the complication rate. Implant infection, capsular contracture and adverse scarring are significant problems for these patients. Doing the mastopexy first and then placing the implants as a separate operation is a much safer option but is very unattractive to patients because it involves two operations which is inconvenient , involves significant downtime and financial expense.
In spite of its problems, augmentation mastopexy has become a common operation and the demand for this procedure increases. It is really important that women understand the risks involved and appreciate the additional scars involved. Because of the pressure from the implant and the lack of elasticity in the skin of many of these women, the scars may stretch and become very obvious.
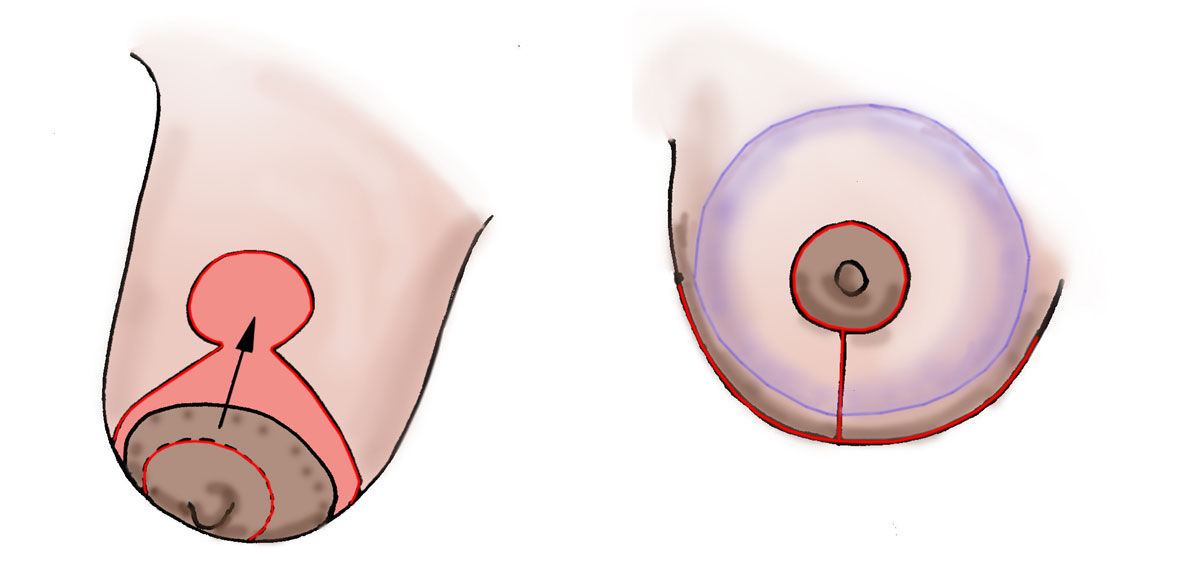
Droopy , low volume breast , showing design of the skin reduction and the result following augmentation mastopexy
Capsulectomy
Capsular contracture is by far the most common complication of breast augmentation with implants. The body naturally forms an envelope consisting of a of thin layer scar tissue around the implant. Most of the time this capsule of scar is thin and pliable. However, in some cases the capsule thickens and starts to contract around the implant. This can happen for a number of reasons but it is thought to be mostly due to a low level contamination of the implant with bacteria (biofilm). Capsular contracture will often spoil the cosmetic outcome and can be uncomfortable.
Total Capsulectomy
To correct this problem the capsule is removed either completely or at least as much as can be easily removed. Ideally the entire capsule should be removed, but in milder cases it is sometimes too risky to remove all of the capsule. This is because the some of the capsule can be adherent to the chest wall and removing every piece can risk puncturing the chest wall, necessitating a chest drain . (Pneumothorax). Also the capsule can be very stuck to the back of the pectoralis muscle and removing it can cause bleeding (haematoma) and increases post-operative pain. If the entire capsule is not removed, the remaining capsule is carefully cleaned and sterilised to reduce the risk of re-contamination and capsular contracture recurrence of the new implant. If the implants are not being replaced , there is no issue and remnants of the capsule reabsorb and disappear.
En Bloc Capsulectomy
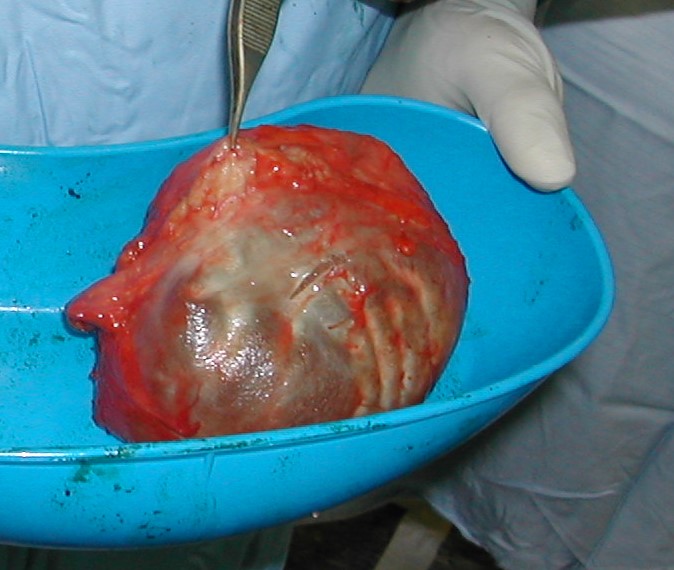
picture of implant removed which is encased in a thick contracted capsule, removed en bloc
There has been a recent trend for en bloc capsulectomy in patients who have Biocell implants and are worried about getting ALCL (see complications). En bloc resection is a term used in cancer surgery and is entirely inappropriate in this context. A much longer incision must be made and the risks of pneumothorax and bleeding are significantly higher. Given that most of the time, the capsule is removed in its entirety – total capsulectomy, this more aggressive approach should be reserved for diagnosed or suspected cases of ALCL only.
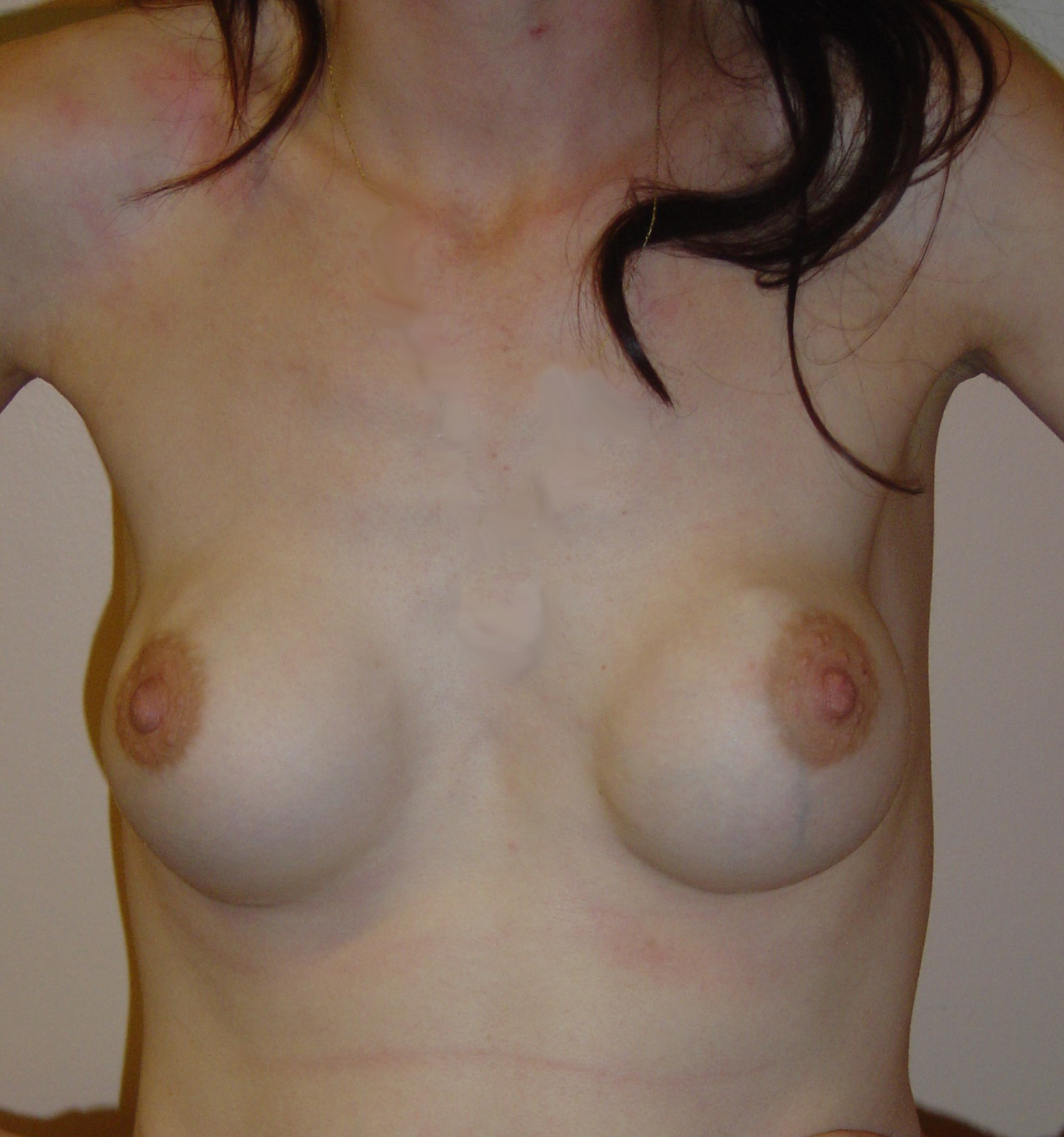
Partial Capsulectomy and Capsuloplasty
Sometimes we take parts of a normal capsule away, or tighten part of the capsule with stitches for aesthetic reasons. Manipulating the capsule like this, can change the position of the implant and /or change the shape of the breast. We do this frequently in breast reconstruction cases but sometimes we do it to revise cosmetic cases if necessary.
